Abstract
The objectives of this study were to determine the frequency and thetypes of errors which occur regarding the preparation and the administrationof medication and to identify the main causes of these errors in a pediatricintensive care unit (PICU) at the University Hospital in Lausanne(Switzerland). In this prospective study, based on the observationof nurses' activities, the data were collected over a period of 10 weeks.The error classification was based on the American Society of HospitalPharmacy (ASHP) definitions.
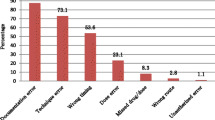
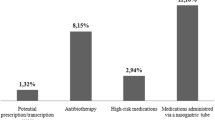
The frequency of errors wascalculated as the sum of all noted errors divided by the total administereddrugs, plus the sum of all omitted drugs, multiplied by 100. The sum of allgiven doses plus all omitted doses gives the 'total opportunity for errors'.This total was 275 and the total frequency of errors was 26.9%. Themost frequent errors were wrong-time errors (32.4%),wrong-administration-technique errors (32.4%) andpreparation errors (23.0%).
In relation with other studiesconducted under comparable conditions, a lesser number of omissions andwrong-time errors were observed. On the contrary, administration-techniqueand dose-preparation errors were more frequent at our hospital.
A program ofsystematic assistance and survey by professional pharmacists could improvethe quality of the preparation and administration of medication in the PICU.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barker KN, Allan EL. Research on drug-use-system errors. Am J Health-Syst Pharm 1995;52:400-3.
Koren G, Barzilay Z, Greenwald M. Tenfold errors in administration of drug doses: a neglected iatrogenic disease in Pediatrics. Pediatrics 1986;77(6):848-9.
Rendell-Baker L. Paraplegia from accidental injection of potassium solution. Letter. Anesthesia 1985;40:912-13.
Zenk KE. Challenges in providing pharmaceutical care to pediatric patients. Am J Hosp Pharm 1994;51:688-94.
ASHP guidelines for providing pediatric pharmaceutical services in organized health care systems. Am J Hosp Pharm 1994;51:1690-2.
Pediatric Pharmacy Practice Guidelines. Pediatric Pharmacy Administrative Group Committee on Pediatric Pharmacy Practice. Am J Hosp Pharm 1991;48:2475-7.
Soumerai SB, Ross-Degnan D. Drug prescribing in pediatrics: challenges for quality improvement. Pediatrics 1990;86(5):782-4.
Barker KN, McConnell WE. The problems of detecting medication errors in hospitals. Am J Hosp Pharm 1962;19:360-9.
ASHP guidelines on preventing medication errors in hospitals. Am J Hosp Pharm 1993;50:305-14.
Allan BL. Calculating medication error rates. Am J Hosp Pharm 1987;44:1046-7.
Tisdale JE. Justifying a pediatric critical-care satellite pharmacy by medication-error reporting. Am J Hosp Pharm 1986;43:368-71.
Rosati JR, Nahata MC. Drug administration errors in pediatric patients. QRB 1983;9(7):212-13.
Raju TNK, Thornton JP, Kecskes S et al. Medication errors in neonatal and paediatric intensive-care units. Lancet 1989;2:374-6.
Nahata MC, Paediatric drug therapy II-Drug administration errors. J Clin Pharm and Ther 1988;13:399-402.
Perlstein PH, Callison C, White M, et al. Errors in drug computations during newborn intensive care. Am J Dis Child 1979;133:376-9.
Bordun LA, Butt W. Drug errors in intensive care. J Paediatr Child Health 1992;28:309-11.
Allan EL, Barker KN. Fundamentals of medication error research. Am J Hosp Pharm 1990;47:555-71.
Barker KN, Harris JA, Webster DB, et al. Consultant evaluation of a hospital medication system: Analysis of the existing system. Am J Hosp Pharm 1984;41:2009-16.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schneider, M., Cotting, J. & Pannatier, A. Evaluation of nurses' errors associated in the preparation and administration of medication in a pediatric intensive care unit.. Pharm World Sci 20, 178–182 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012087727393
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012087727393